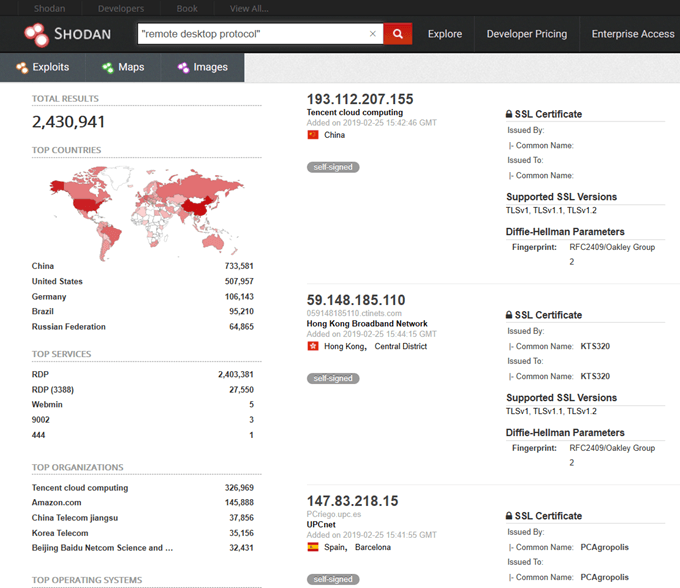
As of Feb 5, 2019, shodan.io shows a total of 2,430,941 computers connected to the internet by way of remote desktop. Out of these, 507,957 belong to computers in the United States. This voluminous number of servers and workstations, depicted in the figure below, are increasingly subject to cyber-attacks.
Since 2016, attacks against the remote desktop protocol have been on the rise. In 2018, the Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3), issued a specific security alert regarding Windows Remote Desktop protocol (RDP).
Attacks related to RDP included ransomware, corporate theft, installation of backdoors, pivoting, and launching of additional attacks. Starting in 2016, black market sales of RDP accounts also became available including identities and login credentials for as little as $6.00 per server.
Obviously, the best way to protect a server is to disable RDP. However, sometimes, this is not an option. If your server is one of the many that requires remote desktop to function, it is paramount to know the types of attacks that may be levied against this protocol and the various methods at an engineer’s disposal to prevent these attacks.
RDP Attack Methodologies
One attack a hacker may utilize is a brute force of RDP credentials. In this attack, a malicious actor will scan a range of IP addresses, look for open ports used by RDP (e.g. 3389), and finally utilize a brute force method such as a dictionary attack to attempt to determine the password.
Unfortunately, not only are credentials subject to loss in this type of attack, but additionally, this brute force attack may serve as a denial of service against the operating system’s memory or storage due to the filling.
Luckily, RDP is encrypted by default through TLS. However, an attacker may still utilize a man in the middle attack to gain RDP credentials. As with any man in the middle attack, the attacker places himself in a broadcast domain shared with either the client or the RDP server.
One such methodology uses a python-based tool called Seth to leverage ARP spoofing to redirect traffic through an RDP proxy. This allows the attacker to downgrade the encryption of the connection and extract clear text credentials.

As with any listening service, attacks may be leveraged against vulnerable code. RDP is no exception to the rule. One example of an RDP specific vulnerability was released to the public as part of CVE-2018-0976.
This CVE notified users of a vulnerability in the remote desktop service which made the operating system vulnerable to a denial of service when specially crafted packets were sent to a listening server running RDP.
An attacker may also utilize his connection through RDP to take additional malicious actions such as the deployment of ransomware, installation of a backdoor, or even pivoting throughout the environment.
In some instances, attackers may tunnel RDP connections through another protocol such as SSH to bypass firewalls and other boundary protections.
Defending Against RDP Attacks
There are several countermeasures an administrator can utilize to defend against RDP based attacks and most are very simple.
Passwords and Lockouts

First, to defend against brute force attacks it is critical to utilize complex passwords or two factor authentication as well as implementing a lockout policy. To implement a lockout policy as part of your windows domain go to the following setting under group policy editor.
Computer Configuration\Policies \Windows Settings \Security Settings \Account Policies \Account Lockout
Set your Account Lockout Threshold to the number of invalid attempts that you choose.
Use an Alternative Port for RDP
To change the port utilize for RDP, alter the following registry key.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp\PortNumber
Install Latest Windows and Security Updates
There are several examples of vulnerabilities in the Remote Desktop software itself. Since 2002, there have been over 20 security updates and 24 separate CVE. Some examples include:
- MS01-052: Invalid RDP Data Can Cause Terminal Service Failure
- MS02-051: Cryptographic Flaw in RDP Protocol can Lead to Information Disclosure
- MS05-041: Vulnerability in Remote Desktop Protocol Could Allow Denial of Service
As with any listening service, it is critical to keep the service patched and up to date to avoid these issues. A full list of vulnerabilities related to RDP was published by Rapid7. It is available at the below link.
https://blog.rapid7.com/2017/08/09/remote-desktop-protocol-exposure/
Restrict RDP Sessions by IP address with Windows Firewall
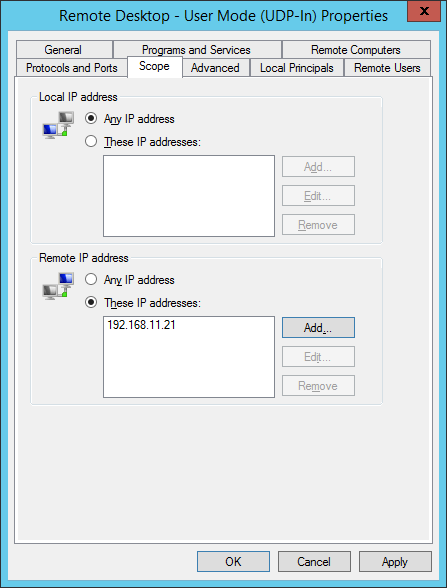
Windows firewall can be used to restrict inbound connections to specific IP addresses only. If you create a firewall rule through the Inbound Rule Wizard, you will see a set of predefined rules available for RDP. Use the TCP and UDP rules.
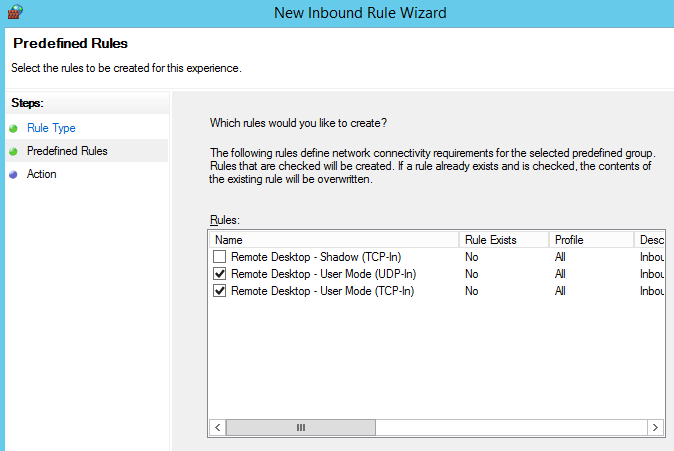
Next, you will need to modify the properties of your rule to restrict inbound traffic. To do so, go to properties and open the scope tab. In this tab, add the allowed IP addresses under remote. Finally, don’t forget to modify the destination port to the port of your choice if applicable.
Turn on Network Level Authentication
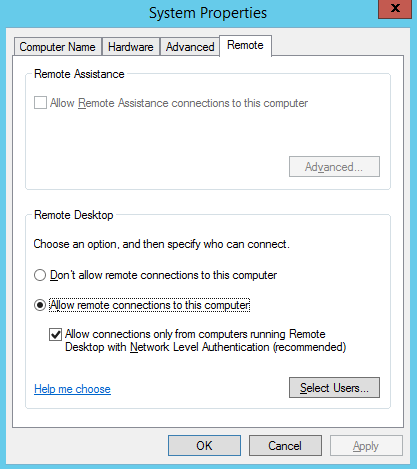
On Windows Vista/2008 and higher, there is a new technology, introduced with RDP 6.0, which aids in the protection of RDP connections. This technology is known as Network Level Authentication.
Network Level Authentication protects an RDP connection by not establishing a full session until the credentials are authorized. In previous versions of Windows, the login screen would load before a full authorization occurred.
This utilized resources and opened the RDP server up to a potential DoS. When setting up RDP, enable NLA by checking “Allow connections only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication. In Windows 7 and later, this setting is checked by default.
Limit Remote Desktop Users
Another protection mechanism available to users of remote desktop is the group policy option for terminal access. From this location, it is possible to limit remote desktop to specific users.
It is recommended to utilize a separate remote desktop specific group of users, rather than allowing all administrative users remote access. To lock down remote users via group policy, do the following:
- Click Start → Programs → Administrative Tools → Local Security Policy.
- Under Local Policies, click on User Rights Assignment, go to Allow logon through Terminal Services. Or Allow logon through Remote Desktop Services.
- Remove the Administrators group and leave the Remote Desktop Users group.
- Use the System control panel to add users to the Remote Desktop Users group.
Use RDP Gateways
An RDP gateway proxies all connections through a single gateway server. This service is built in on Windows 2008 and 2012. The gateway will listen for terminal services requests over https and then connect the client to the RDP server.
This forces all connections to be monitored via a central location. Directions to set up a remote gateway are available at the following link:
Tunnel Remote Desktop Connections through IPSec or SSH
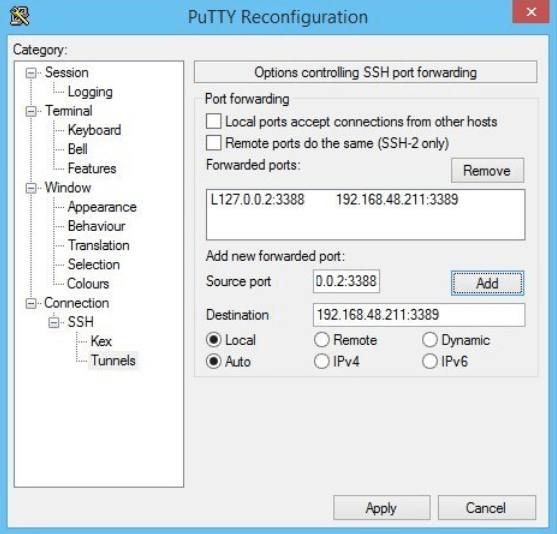
An additional security precaution can be taken by tunneling RDP sessions through IPSec or SSH. One simple way to accomplish this is with putty. First, connect to a remote ssh server local to the RDP server.
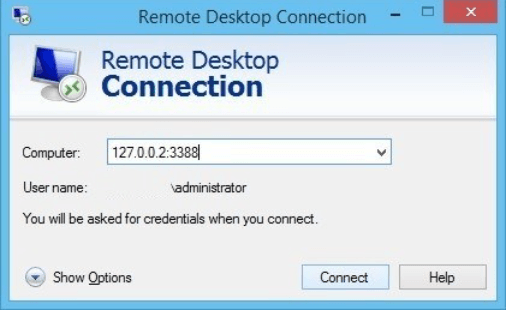
Next, set up the client putty ssh session as shown below. Under Connection | SSH | Tunnels, you will set up port forwarding from 127.0.0.2:3388 (or port of your choice) to the RDP server IP and port.
Finally, connect your RDP server to the local address and port. This will port forward through an SSH tunnel to the final destination.
Summary
Remote Desktop attacks are increasing on a yearly basis. There are several RDP attack methodologies utilized by malicious actors today including brute force, man in the middle, and exploitation of vulnerable code.
Hackers also utilize RDP as a deployment mechanism for other attacks such as ransomware. Despite the various attack vectors, when implemented properly, RDP can still be utilized safely.
Ways to protect RDP include limiting connections to specific IP addresses and users, keeping RDP updated and patched, utilizing RDP gateways, implementing tunneling over SSH, utilizing Network Level Authentication, and obscuring the RDP port.
It is also important to use complex passwords, two factor authentication, and account lockouts. RDP can be a useful tool when used correctly. It can be implemented fairly securely if all the precautions above are in place.